Kraken is a San Francisco-based digital-currency exchange founded in 2011 in the wake of Mt. Gox’s collapse. It is the 10th largest exchange by 24-hour trading volume, according to CoinMarketCap. Kraken was also the first Bitcoin exchange to have its trading price and volume displayed in the “Bloomberg Terminal”. The co-founder and CEO of the company is Jesse Powell.
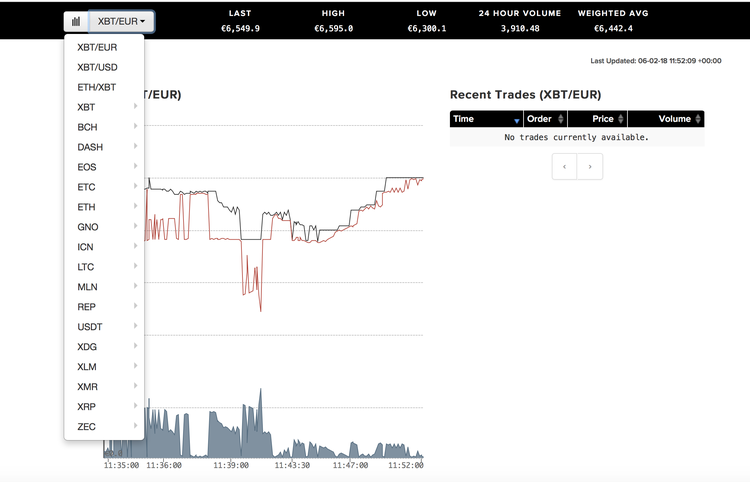
Cryptocurrencies available
Kraken is a trading platform with many advanced features, such as quick deposits and withdrawals, stop-loss and stop-loss limit, trailing stop, trailing stop limit, take profit limit, stop loss take profit limit, leverage, and margin trading. While not unsuited for beginners, Kraken is more focused on advanced traders, and its advanced tools will serve them better.
The platform has about 60 trading pairs, including various fiat ones, such as the U.S. dollar, Canadian dollar, British pound sterling, Japanese yen, and euro. The most popular cryptocurrency offerings are in Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ether, Litecoin and more.
Verification
Like all regulated exchanges, users will have to verify their identity and personal details before buying.
Kraken offers different levels of verification for the accounts, otherwise known as Tiers.
Tier 0 - this is the default Tier obtained after registering an account and confirming the email address. It allows look around to get the feel of the interface and platform, but no deposits, withdrawals or any trades can be made.
Tier 1 - deposits and withdrawals are allowed in digital currency only. Trading, however, is enabled in digital as well as fiat currencies. Full name, date of birth, country and phone number are required.
Tier 2 - users can deposit, withdraw and trade in digital currency, and depending on the country of residence, fiat currency funding may be accessible. Bank deposits and withdrawals are available to clients in some areas at this Tier. Providing the physical address is required.
Tier 3 - fiat currency funding is available to Tier 3 clients and funding limits are much higher than Tier 2. Users are required to upload an identity and proof of residence document.
Tier 4 - like Tier 3 but with even higher funding and trading limits. This Tier is available to high-volume individual or corporate traders. The required documents for Tier 4 individual accounts include a signed application form and KYC documents.
How to Trade on Kraken Exchange
Trading on the Kraken platform can be performed by exchanging fiat currency for cryptocurrency, or one cryptocurrency for another. Kraken supports deposits and withdrawals in EUR, USD, GBP, JPY and CAD.
Kraken is both a “spot exchange” for exchanging between currencies, and a Forex-like market for “currency pair trading” (CPT) on leverage. While utilising Kraken as a “spot exchange”, one must have adequate funds in one currency to exchange for another such as depositing USD in order to exchange for XBT on the XBT/USD pair. After executing a spot exchange between currencies the funds are available to be exchanged again or withdrawn.
In currency pair trading, however, the leverage feature is used. While trading on leverage users are only required to hold collateral currencies and are able to trade any of the margin pairs even if they do not hold the currency on that pair. Currency pair trading allows to open short or long positions using leverage. Trading short is only possible with leverage, which means it’s only possible on margin pairs.
Some pairs will only be available for spot exchanging and not leveraged trading. Also, there can be currency pairs that can't be exchanged on spot, but can be traded as a positions using leverage, so one may only have the option to select a level of leverage for some currency pairs.
To summarise, a “Spot Exchange” is defined by exchanging one currency for another while “Currency Pair Trading” is borrowing funds using collateral on the account in order to open up a position using leverage to short or long a currency against another currency.
Fees
Fees on Kraken are charged on a per-trade basis. Fees are calculated as a percentage of the trade's quote currency volume (by default). Certain pairs allow the fee to be calculated based on the trade's base currency, which can be specified when ordering using the Fee Currency option.
User fee volume levels are measured using the equivalent market value of the listed "Fee Volume Currency" at the time of the trade. User fee volume levels are measured and applicable for trades occurring in the last 30 days only. For detailed information on fees click here.
About the security
The platform is considered to be one of the most secure destinations for cryptocurrency trading. Kraken has a mobile app available for iOS devices. It uses cold storage techniques for added security and also uses PGP/GPG encryption. Users are encouraged to use the 2-factor authentication feature to get even more security for their accounts.
According to The Fortune, customers of Kraken recently experienced connection problems caused by record-level trading volumes. All trading and withdrawals were suspended during the maintenance which was projected to last two hours but the process didn’t go smoothly.
Nevertheless, everything turned out fine. The exchange finally came back online after two days, with all client funds reportedly intact. Kraken noted that those troubles were caused primarily by continually increasing demand. The company acknowledges that it was overwhelmed by about 50,000 registrations per day with close to 10,000 new support tickets. As a kind of apology to users, Kraken reduced non-margin trading fees to zero until the end of the month.
The clash with New York and plans of going public
Kraken Exchange will “probably” register with US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as a broker-dealer and an alternative trading system (ATS).
Earlier this year, the SEC issued a bulletin warning cryptocurrency exchanges not to list security tokens without registering as a national securities exchanges and threatening to pursue enforcement action against platforms that list unregistered securities.
“We would probably get registered as a broker-dealer and then an ATS,’’ Jesse Powell told Bloomberg in an interview in New York. “I don’t think it necessarily helps the business. I think we’re doing everything right anyway.’’
Kraken currently operates in the US as a money transmitter business, which is regulated at the state level. Being labeled an ATS would bring Kraken more directly under the SEC’s oversight.
It is worth mentioning that the digital-currency exchange had refused to respond to inquiries from New York’s top lawyer who had sent letters to Kraken and a dozen other crypto exchanges seeking information on their internal controls and how they protect customers. Powell dismissed the request, calling the inquiry “insulting”.
Despite Kraken’s clash with New York, the company appears open to working with federal regulators. Moreover, the platform is also considering getting into stock trading, and potentially going public down the road.
“If we could find a way to do that -- to have the company’s stock traded as a token, I think that would be awesome,” Powell said.
Suspending operations in Japan
Kraken Exchange is suspending its operations in Japan due to rising costs of maintaining its business there but indicated it could return in the future.
“Suspending services for Japan residents will allow us to better focus on our resources to improve in other geographical areas. After we have had a chance to better catch up to our rapid growth, we will consider the possibility of resuming service for Japan residents,” Kraken said in a statement, CNBC reports.
The company noted that the decision involved careful consideration of revenue against the costs and resources required to maintain service.
It is worth mentioning that Kraken’s decision to suspend operations comes at a time of government crackdown for exchanges.
According to Investopedia, the theft of $534 million worth of NEM at Coincheck, one of Japan’s largest exchanges, earlier this year was the trigger for exchanges to form a self-regulatory organization. The government also began suspended operations for two exchanges and warned five others for failing to institute checks and balances in their IT systems that prevented hacks and criminal use of digital money.
By Bob Loxley