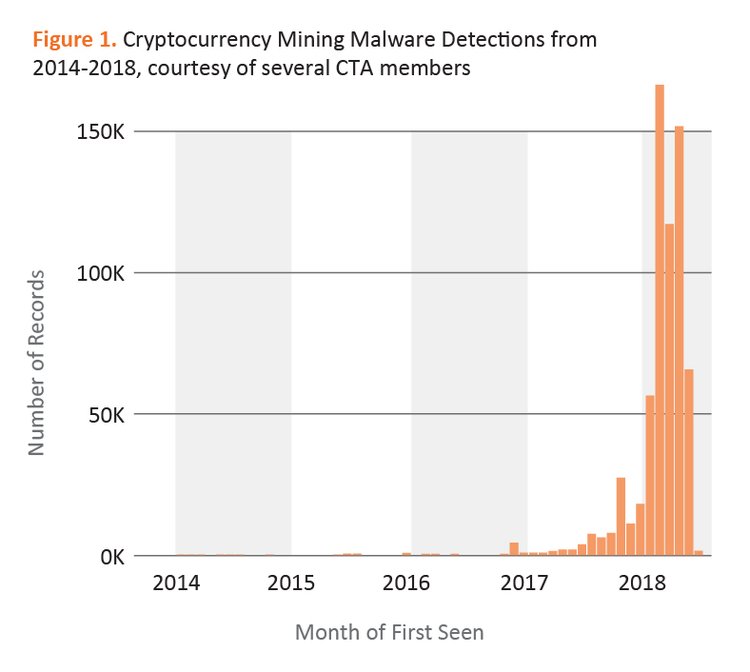
A Cyber Threat Alliance (CTA) conducted an analysis of illegal cryptocurrency mining. The combined data of several CTA members show an increase of 459% in the detection of malicious mining programs since 2017.
An increase in the number of malicious programs in the mining industry is due to the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies. Even despite the high volatility of the crypto market, the value of digital assets attracts cybercriminals. At the same time, CTA notes that individuals and business representatives have underestimated such attacks.
Therefore, researchers urge everyone to pay closer attention to the illegal mining and understand what threats such actions of cybercriminals are causing. The illegal mining of cryptocurrencies results in a leakage of enterprise resources, increases the burden on computers and other equipment, damages IT infrastructure. All of this leads to an increase in electrical bills and a decrease in the computer performance.
СTA calls to pay attention to the phenomenon, which they call "canary in the coal mine". This means that the hidden mining indicates the overall vulnerability of the system. "If miners can gain access to the processing power of your networks, then you can be assured that more sophisticated actors may already have access," the report says.
According to the report, as of July of this year, 85% of all illegal cryptocurrency threats are aimed at Monero mining. Bitcoin accounted for about 8%, while other cryptocurrencies accounted for only 7%.
In this case, the most common way for the hidden mining of Monero remains Coinhive. A special script is installed on the site and then launched into the visitors' browser. Thus, resource owners refuse, for example, from displaying ads on the site. However, Coinhive is widely used without informing users. Sometimes, the owner of the resource does not know about the script, as was the case with the recent attack on Facebook Messenger and Starbucks Wi-Fi. As of July 2, PublicWWW has left at least 23,000 sites that host the Coinhive code.
The analysis also noted that the exploit EternalBlue still affects the business. The patch was originally developed by the U.S. National Security Agency, but the hacking Equation Group stole it and began selling it to everyone. Most of all, the exploit is known for its role in the global infestation of computers with an extortion software WannaCry and NotPetya.
Researchers also note that cybercriminals are becoming more advanced and are using new methods. Analysts have observed “successful and widespread attackers “living off the land,” or employing legitimate functionality to download and execute miners that would be more difficult for an observer or antivirus to detect, such as the profitable and widespread Monero-mining campaign Smominru.”
In general, CTA hopes that the new analysis will help in the fight against illegal mining. Anyone who examines the report will be able to successfully withstand cyber threats and improve their defensive positions in this direction.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel to stay up to date on the latest crypto and blockchain news.