Living in today’s reality many of us question what the future holds for humankind. The first things that come to mind are the global issues: Diseases, hunger, greenhouse effect… and is there a solution to all of this? And some are just curious of what the futuristic fridges of ours will store and wondering what exactly they will be eating.
Just like a pill
Oh, that question “what to eat?” forms probably 80% of human relationships, all that time we spend on cooking, money we spend on food? The idea that just one tablet a day would keep all those problems away is really inspiring. I would like to upset you though, but the possibility of this solution coming to life is highly doubtful. Let’s just do the maths. An average man requires about 2500 kcal per day, the female needs a bit less — 2000 kcal. A combination of various sources of energy (fats, carbohydrates, and proteins) is recommended by nutritionists for a healthy life. In fats, the most concentrated food source, there are about 9 kcal/g, and carbohydrates and proteins contain about 4 kcal/g.
Large pills weigh about a gram, that is, the average man must eat 521 tablets, and a female — 417 tablets daily to meet basic energy needs. In this case, necessary vitamins and minerals are not included in the layout. But don’t worry, there are so many thrilling food improvements scientific world is developing for the future.
Take a sniff of that
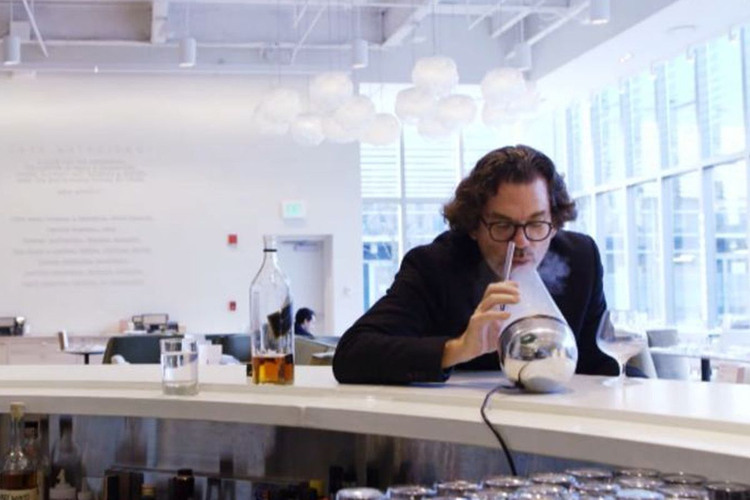
Our metabolism is playing tricks with us. At the age of 20 we can get away with eating pizzas and kebabs without gaining any extra weight, but when we get older it seems that we gain few pounds after simply touching or breathing near a small piece of chocolate. And that is not just a figure of speech by the way! It’s actually possible right now and in the future, it might be one of the common nutrition plans. The creator of edible packaging David Edwards created a device called Le Whif which sprays inhalable dark chocolate. Mmm... smells delish.
The innovative nutrition tends to control your intake. The product already became a bestseller, and consumers declare that the device helped them to cut down on eating sweets. On the base of this device, a Canadian chief made some improvements adding a built-in ultrasonic generator which turn food (mainly soups) into a fog. Using a straw consumers can inhale the fog and distinguish the taste of the dish and even individual ingredients. What an interesting diet to experience! You only gain 200 calories per 10 minutes.
Eco is the new black
Back to the creation of a Harvard University professor David Edwards and his edible packaging. Keep your imagination at bay here, it does exactly what it says on the tin... 1/3 of the waste on the planet is packaging, most of it, is not even recycled. The eatable package will reduce the waste dramatically. Moreover, the innovation reduces food waste and also diminishes a chance of food-related infections. Edwards created a material similar to the grape skin which is fully eatable, keeps food and drinks fresh and preserves them from bacteria and other substances.
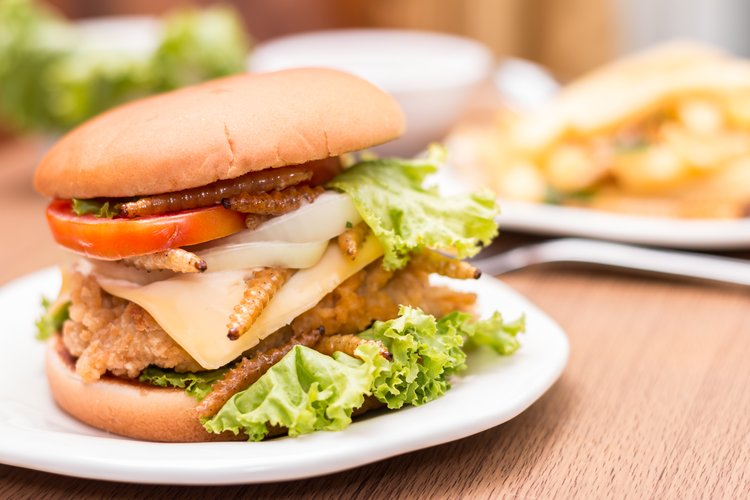
Another nasty eco-friendly product which already saved lots of people around the world from hunger suffering is... insects. Yes, a lot of futurists and scientists claim that in the future insects will replace meat and become the main source of protein for humans. The argument that insects are much easier to cultivate and additionally produce fewer greenhouse gasses (9 g comparing to 2,5 kg per 1 kg of meat). The ones, who keen on food cultivated in-house, could even get a futuristic desktop farm for edible fly larvae. What a handy solution, no need to spend time on supermarkets and you will cut on petrol spending as well! Although such a delicacy is not quite acceptable to the western mind and taste, environmental conscious scientists, opinion leaders, and chiefs are looking for ways to overcome preconceived vision for future generations. There are already lots of cafes and restaurants around the world where you can try out an insect meal.
The science behind our food
If you are not ready to eat insects and sacrificing juicy burgers for the environment is also not an option, the solution is coming to the market soon. Scientists are working to create a new way of meat production and take food availability under total control of people and technologies. Test tube meat which is grown in the lab will save humanity from waste and over pollution, and animals from suffering. The first meat burger grown from cow stem cells was fried at a press conference on August 5, 2013. But don’t be excited just yet, as the price of such cutlet is about $325 thousand.
Here, a less of a humane statement, which could potentially bring something new to our table: “If you cannot fight them, eat them,” and it concerned jellyfish in the Mediterranean and Black Seas. Officials noted a reduction in fish populations and a growing number of jellyfish. One of the suggestions is the use of jellyfish in the food and medical industries. Recently ice cream makers ‘Lick Me I'm Delicious’ came up with a bright idea to add a recreated jellyfish protein which they got from a laboratory to their product. Would you be surprised to hear that it glows when exposed to external influences? Magic! A new ice cream shines when it’s being eaten.
Algae is another natural nutrition which is now coming into the mass food production. It contains a high amount of Omega-3 acid which benefits our health. The supply of the algae is abundant as its produced in fresh water. There is an invention which allows growing algae by ... breathing was presented during the performance of the opera singer in V&A museum in London.
Late in 2013 NASA announced the development of 3D food printing technology. The idea is to variegate boring meals in tubes for astronauts by printing out dishes. The initial goal of the joint project of the space agency and the ambitious engineering bureau from Texas was to cook a pizza using a 3D printer, and they achieved their goal. And at some point in the future, it will be available to the market. Imagine how taught life on campus will be when you need to queue not only to print out the coursework but food as well... Scientists from Cornell University (New York) are not lagging behind their colleagues and are developing technology, which will allow using hydrocolloids (instead of “ink”) to print almost anything: chocolate, veggies, mushrooms, apples, boiled chicken, banana, boiled macaroni, fresh cheese, tomatoes, boiled yolk and much more. According to promises, the food will be much healthier and people will have perfect balances nutrition.
The scientific world is focused on working on nanotechnologies and genes and one of the key issues of note is food. The main reason for genetic modifications of crops is to achieve yields that have increased resistance to diseases and parasites. But it is not the only reason, and as the tech progress is chasing the ideas of how the modified food can benefit us. Scientists now are able to edit the genome with a terrific accuracy: scientists use it to grow apples that don’t get dark over time, smooth virus-less pigs and etc. For many, the abbreviation GMO is still a reason to put a product back onto the shelf, however, such products have long been a part of our meal plan and the tech future will bring new ways of food management and ways of creating new variants.
With numerous ideas from scientists, technological progress and futurists, the picture of future food is still quite undetermined. Some are imagining pictures from the futuristic books where the characters are eating air, modifying genes of everything that moves… and growths. However, there is also a trend of returning to long-forgotten cereals (like millet and farro), which, as it turned out, is more resistant to extreme weather conditions, as well as more nutritious and healthy.
Organically grown foods will also increasingly start moving from the suburbs to the city, as of 2050 about 70% of the population will live in the cities. Today, city farms already exist in the courtyards and on the roofs of residential and office buildings. For instance, Japan is already setting the trend by building an office building that includes 4,000 square meters of farms where rice, fruit, and vegetables grow. Crops are grown under special lamps, using automatic sprinklers, hydroponic plants, and climate control systems. All products are served in the cafe to the employees.