As the innovative blockchain technology continues to find an increasing use across multiple business sectors, more and more global companies explore the technology first inspired by Bitcoin.
A recent study published by IPRDaily revealed that China and the U.S. are leading the global drive to develop blockchain applications.
According to the research, which ranks companies based on the number of patents filed, Chinese e-commerce giant Alibaba tops the list with a total of 90 applications, followed by the computer giant IBM (89 patents) and global payments leader Mastercard (80 patents).
Alibaba
In the most recent development, Alibaba Cloud, a cloud computing arm of Alibaba Group, has expanded its Blockchain as a Service (BaaS) offering the major global markets including South East Asia, the U.S., and Europe.
Based on two blockchain network implementations — Hyperledger Fabric and Ant Blockchain — Alibaba Cloud’s BaaS — are now allowing global enterprises to set up a secure and solid ecosystem for blockchain developments, the press release notes.
BaaS supports a wide range of applications including automatic deployment, consortium blockchain management, smart contracts, user and certificate management, and SDK (Software Development Kit) applications, as well as a range of monitoring, operating and maintenance functions, the company said in a press release.
Earlier this year, Ant Financial — the payment affiliate of Alibaba, launched a blockchain-based cross-border settlement service for consumers. The service was initially rolled out for consumers sending funds between Hong Kong and the Philippines.
Ant Financial then said that integrating its AlipayHK service with GCash — a Philippines-based mobile payment service — using blockchain tech, would save users from having to go to intermediaries and that it would settle their transactions within seconds.
In August, Technote reported that Ant Financial had been secretly experimenting with blockchain technology applications by sending out nearly 600,000 blockchain electronic medical bills to patients over two weeks.
Jack Ma’s company has recently filed a patent application with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) for a blockchain-based system that allows a third-party administrator to intervene in a smart contract in case of illegal activities.
The patent document, which was initially filed in March, describes a blockchain-powered transaction method that enables authorized parties to freeze or halt user accounts associated with illegal transactions, or intervene in a blockchain network.
In April, Alibaba teamed up with four companies from Australia and New Zealand to introduce a food-tracing system based on blockchain technology to combat food fraud.
With the help of Food Trust Framework, the consortium looks to use blockchain to improve integrity and traceability on its global supply chains.
IBM
The U.S. tech giant IBM has established itself as a leader for innovative blockchain solutions around the world.
Just recently, IBM and the Dubai government announced the launch of the Dubai Blockchain Platform, the first government-endorsed blockchain platform-as-a-service in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
The platform is designed to help local companies in the transition of blockchain testing and development into full production and digitize government services.
Two years ago, IBM launched theIBM Blockchain Platform, a public cloud service that customers can use to build secure blockchain networks.
Built on the Hyperledger Fabric, IBM Blockchain is designed to accelerate, through collaboration in each phase, the creation of "built for business" global blockchain networks with the performance and security for even the most demanding use cases and regulated industries.
IBM Blockchain Platform provides different membership plans to help all types of users get started on their blockchain journey and move their applications into production.
“Solutions built on the IBM Blockchain Platform can trace food in seconds instead of days, speed shipments through a single and secure view of the truth, and help bypass an outdated international payments system with simultaneous clearing and settlement of cross-border transactions,” reads a post on the platform’s website.
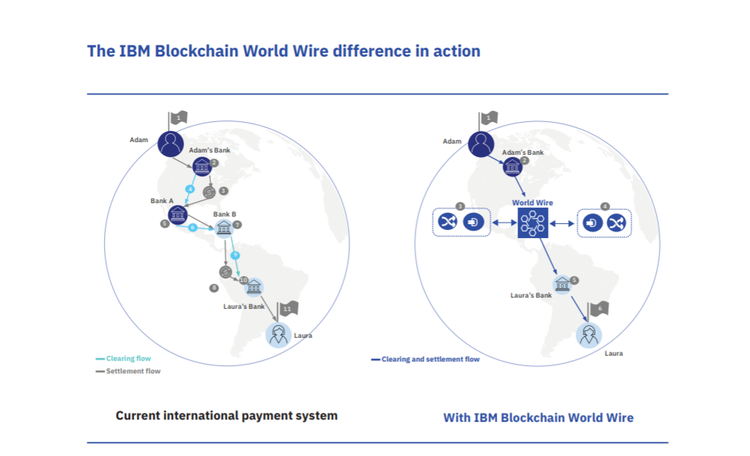
IBM has developed the IBM Blockchain World Wire — a cross-border payment settlement system that makes it possible for financial institutions to clear and settle cross-border payments in seconds.
How does it work? Two financial institutions transacting together agree to use a stablecoin, central bank’s digital currency or other digital coins as the bridge asset between any two fiat currencies.
Institutions use their existing payment systems — seamlessly connected to the World Wire’s APIs — to convert the first fiat currency into a digital asset.
World Wire then simultaneously converts the digital asset into the second fiat currency, completing the transaction. All transaction details are recorded onto an immutable blockchain for clearing.
IBM has also launched the IBM Food Trust - a network that uses blockchain technology to create unprecedented visibility and accountability in the food supply chain by connecting growers, processors, distributors, and retailers through a permanent and shared record of food system data.
IBM is now looking to bring an “Uber-like” blockchain solution to the mining sector that can track minerals from the mine to the market, Stockhead reports.
Citing the Food Trust product, IBM blockchain boss Juergen Kuebler said: “We can trace everything from the farm to the table, whether it is temperature control the entire way or not. So we have these abilities and we will deploy them in an Uber for logistics scenario for the mining industry.”
Mastercard
Mastercard has long embraced the blockchain technology but has now filed a patent for what seems to be a centralized cryptocurrency. Mastercard wants to apply principles of fractional reserve banking to cryptocurrencies.
The company hopes to create a system, which will “protect consumer and merchant information and credentials” while simultaneously “storing a plurality of account profiles.”
They also want “centralized accounts to manage fractional reserves of fiat and blockchain currency updated via transaction messages corresponding to fiat- and blockchain-based payment transactions.”
Thus, Mastercard actually plans to build a cryptocurrency that has all the benefits of blockchain technology, minus the highly sought-after feature of decentralization.
Exactly a year ago, Mastercard unveiled its own blockchain network to enable partner banks and merchants to make cross-border payments faster and more securely.
The four key differentiators of the Mastercard Blockchain include privacy, flexibility, scalability, and the reach of the company’s settlement network.
Mastercard blockchain solution has the ability to power secure and seamless non-card payment transactions such as business-to-business payments and trade finance transactions. It can also power non-payment solutions such as proof of provenance that helps authenticate products across the supply chain.