What are the technologies that are going to drive the future? Below are the three technologies many expect will go mainstream in the coming years.
Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) has long been talked about as the next big innovation in home technology.
IoT defines a network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items that connect people, systems and other applications to collect and share data.
In the broadest sense, the term IoT encompasses everything connected to the Internet, but it is increasingly being used to define objects that "talk" to each other. The IoT is expected to connect many of the devices we have at home, from smart microwaves to smart fridges.
Research and advisory company Gartner predicted as early as 2014 that 25 billion connected "things" will be in use by 2020.
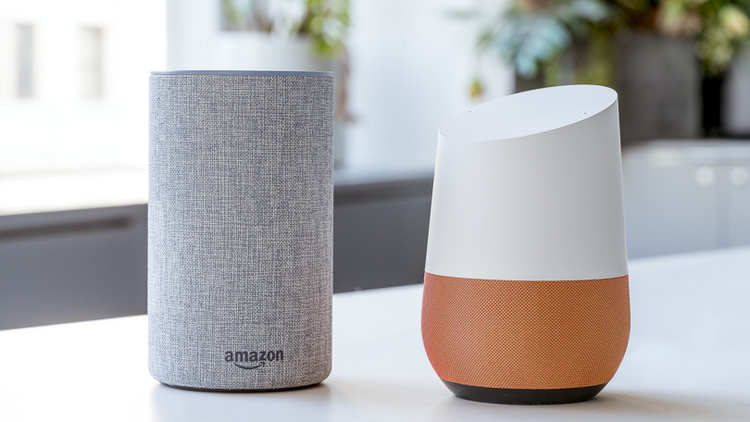
Google Home and Amazon’s Echo are examples of the real-life use of IoT. Google Home is a brand of smart speakers that enable users to speak voice commands to interact with services through Google's intelligent personal assistant called Google Assistant. The Amazon Echo speakers, in turn, are devices connected to the voice-controlled intelligent personal assistant service Alexa.
Apple and Samsung have rolled out the HomePod and Bixby technology respectively to compete with the success of the Google and Amazon systems.
Furthermore, the Internet of Things is now wearable. Companies like Google and Samsung have invested heavily in building wearable devices installed with sensors and software that usually offer biometric measurements such as heart rate, perspiration levels, and even complex measurements like oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
Smart city is another powerful application of IoT. IoT applications for smart cities include smart surveillance, automated transportation, smarter energy management systems, water distribution, urban security and environmental monitoring. Microsoft is one company that offers to “create safer, more efficient cities by transforming infrastructures, buildings, and services with Internet of Things (IoT) solutions.”
The Internet of Things is becoming increasingly popular in spheres such as agriculture, energy, healthcare and many others. Internet-connected clothing is expected to be the next step. The industry is yet to go mainstream, but everything from biometric shirts to contactless payment jackets are already on sale.
Blockchain
When one talks about technology that could potentially change the way we live, blockchain is perhaps one of the first things that comes to mind.
The brainchild of a person or group of people known as Satoshi Nakamoto, the blockchain is an undeniably ingenious invention.
Blockchain - the peer-to-peer, decentralized, distributed ledger - has long evolved from solely being the technology behind Bitcoin. Blockchain technology is applied for innovative social projects in many areas such as decentralized and cloud services for healthcare support, patient records, supporting microfinance transitions and guarantees, cloud-based learning and much more.
What makes the blockchain universal is how it can be implemented for just about any kind of transaction, record-keeping or agreement between one or more parties. Though many people associate blockchain technology solely with cryptocurrency transactions, it can be used to record any type of exchange — for example, property sales, audit data, voter identification, or supply chain origin.
As long as there is information that represents an agreement or record, the blockchain can record, encrypt and protect that information for eternity.
Blockchain is believed to be a game changer for supply chain management. Managing today’s supply chains is extraordinarily complex, and the blockchain is called to solve the issue by helping enhance transparency, preventing counterfeits and thefts, improving regulatory compliance, reducing paperwork and cutting costs significantly.
At the beginning of this year, De Beers – which mines, trades and markets over 30% of the world’s supply of diamonds – announced that it will create the first blockchain ledger for tracing stones from the point they are mined right up to when they are sold to customers.
Identity security has been one of the major problems in the age of Internet, as ownership of data is largely in the hands of the countless applications and services that we grant consent to. Blockchain can solve problems with digital identity, by giving control back to the user, so called self-sovereign identity.
Civic is an example of blockchain-based identity theft protection platform that seeks to provide every person on Earth with a digital identity that they can use to interact privately and securely with the world. Civic is an identity management service that allows to protect and authorize the use of anyone’s identity in real time.
Blockchain can also help alleviate problems within healthcare by serving as a secure database on which patient medical records can be stored. Thus, Medicalchain uses blockchain technology to securely store health records and maintain a single version of the truth. Different organisations such as doctors, hospitals, laboratories, pharmacists and health insurers can request permission to access a patient’s record to serve their purpose and record transactions on the distributed ledger.
These are just a few examples of blockchain use cases, which span across a wide range of areas, including voting, smart contracts, energy market, charity, real estate, cybersecurity, insurance and many more.
While many are not enthusiastic about the future of cryptocurrencies, most believe blockchain is here to stay.
Artificial Intelligence
The rapid pace at which artificial intelligence (AI) is growing has brought about heated debates over the technology’s potential threats and opportunities.
Some fear AI could come to dominate over humanity and insist on the necessity of more control over the technology.
The world-renowned physicist Stephen Hawking was among those concerned that artificial intelligence could replace humans.
“If people design computer viruses, someone will design AI that improves and replicates itself. This will be a new form of life that outperforms humans,” the late scientist once told The Wired.
Even Elon Musk, known for his futuristic gambles, fears that intelligence smarter than human’s — could create an "immortal dictator."
The Tesla and SpaceX CEO says Artificial Intelligence is a “greater risk to the world than a nuclear conflagration with North Korea” and even predicts that AI could be the cause for the Third World War.
Nevertheless, from SIRI to self-driving cars, artificial intelligence is progressing rapidly. High-profile examples of AI include autonomous vehicles such as drones and self-driving cars, medical diagnosis, creating art, proving mathematical theorems, playing games, search engines (such as Google search), online assistants (such as Siri), image recognition in photographs, spam filtering, etc.